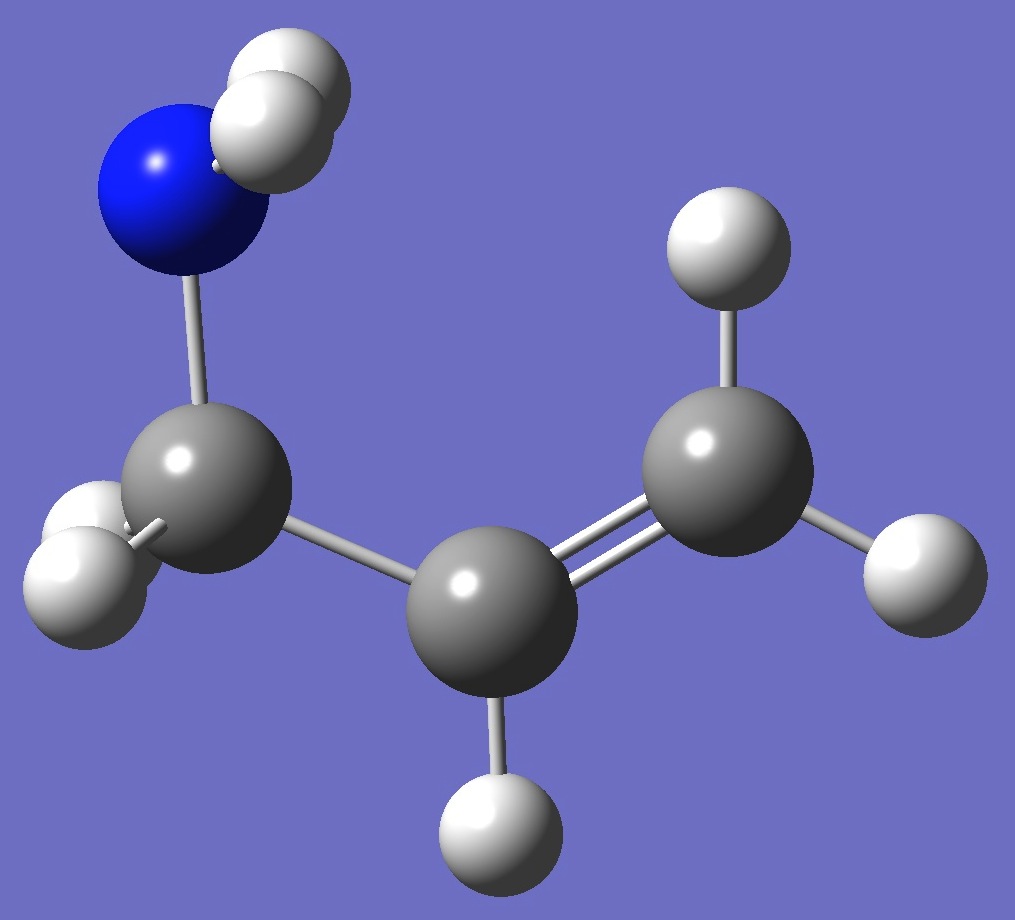
Allylamine is an organic compound with the formula C3H5NH2. This colorless liquid is the simplest stable unsaturated amine.
Production and reactions
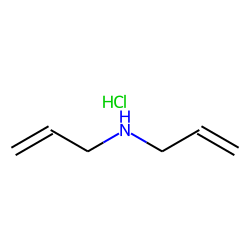
All three allylamines, mono-, di-, and triallylamine, are produced by the treating allyl chloride with ammonia followed by distillation. Or by the reaction of allyl chloride with hexamine. Pure samples can be prepared by hydrolysis of allyl isothiocyanate. It behaves as a typical amine.
Polymerization can be used to prepare the homopolymer (polyallylamine) or copolymers. The polymers are promising membranes for use in reverse osmosis.
Other allylamines
Diallylamine is a precursor to industrial products. Functionalized allylamines have pharmaceutical applications. Pharmaceutically important allylamines include flunarizine and naftifine; the latter spurred the development of Petasis' borono-Mannich reaction. Flunarizine aids in the relief of migraines while naftifine acts to fight common fungus causing infections such as athlete's foot, jock itch, and ringworm.
Safety
Allylamine, like other allyl derivatives is a lachrymator and skin irritant. Its oral LD50 is 106 mg/kg for rats.
References
External links
- Allylamine from PubChem at National Center for Biotechnology Information